As part of the on-going improvements in MetaKarta, many import bridges are updated to import the source metadata at multi-models, rather than huge single models. This improvement is implemented to ensure that there are no size limits when importing from exceedingly large sources.
A good example of this improvement is in the database based bridges. For example, a Hadoop based data lake may have thousands of databases each with many thousands of data elements (tables/columns). If imported as one model, this source becomes unwieldy. However, upgrading the bridge so that it imports each database as a separate model, means the object is a multi-model, and each model within is of a manageable size.
In general, one is going to first migrate from an earlier major release of MetaKarta where database model objects were single-model only, to a newer version of the product where database model objects are multi-models. Thus, first you must follow the instructions to upgrade to the new version of in MetaKarta. Then, you will have a number of database model objects which are single-model imported models which must be migrated.
The migration may be performed on a per model basis or on a folder or the entire repository. This last option is the recommended route. The process will create new configurations based upon the existing ones for each configuration which contains one or more single model(s) that are migrated.
The elements which are migrated include:
o The imported model itself is re-harvested as a multi-model
o Term classifications
o Semantic mappings
o Stitchings
o Custom Attributes
o Comments and Social Curation
o Table level Relationships.
As part of the migration from single to multi model, certain structural data elements will change:
o Schema -> Database Schema
o Database -> Database Server.
This means that any custom attribute on Schema or Database objects cannot migrate until those same custom attributes are also assigned to the new structure data element (either Database Schema or Database Server).
Steps
1. Go to MANAGE > Custom Attributes.
2. Select a custom attribute from the list which applies to either Scheme or Database.
3. Click CHOOSE next to Scope and include either Database Schema or Database Server.
4. Finish all the other custom attributes from the list which applies to either Scheme or Database.
5. Go to MANAGE > Repository
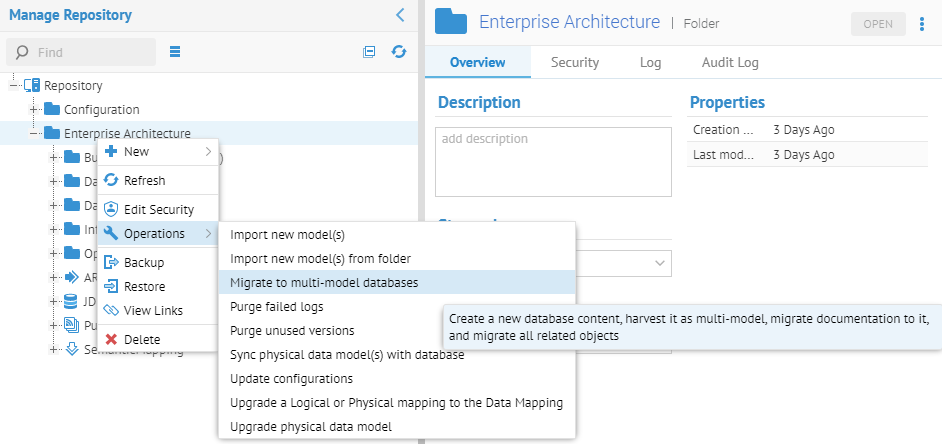
6. Right-click on the Repository at the root of the tree and select Operations > Migrate to multi-model databases.
Example
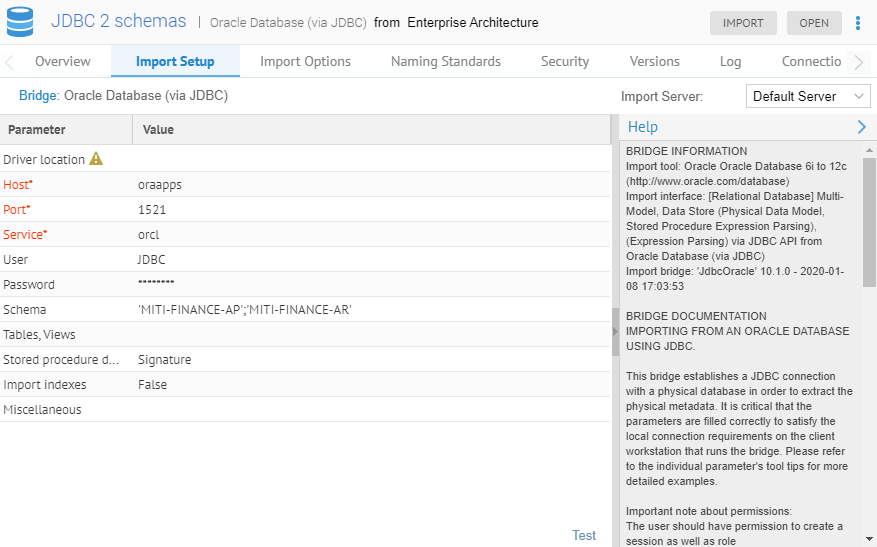
For this example, we used a special import directly from Oracle with two schemas (Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable) rather than separate models from SQL Server DDL.

We ensure that we are creating a single-model database model by NOT specifying “-multi-model” in the Miscellaneous bridge parameter.
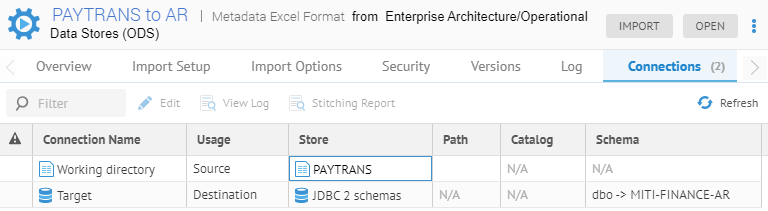
Note, this model is stitched to the existing PAYTRANS and Staging DW data stores.
Mapped using a data mapping to the Staging DW model.
The ADDRESS table is mapped semantically from the Finance glossary.
The CUSTOMER table is classified
The CUSTOMER table is commented on, certified, endorsed and warned, and has custom attribution.
Now, let’s migrate. Go to MANAGE > Repository and Right-click on the Repository at the root of the tree and select Operations > Migrate to multi-model databases.
The log presents any issues found.
There is a folder structure with the older configuration, before migration.
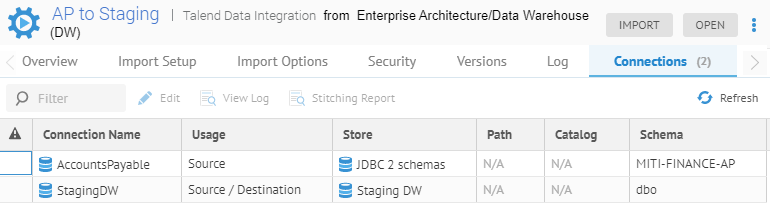
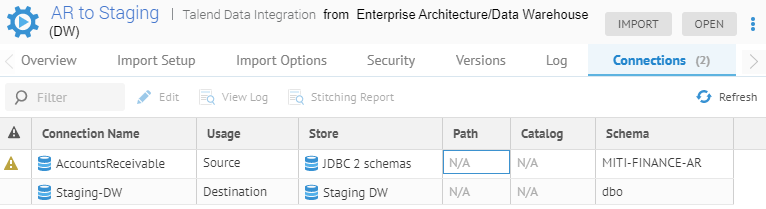
In the new configuration, we have this new model is stitched to the existing PAYTRANS and Staging DW data stores.
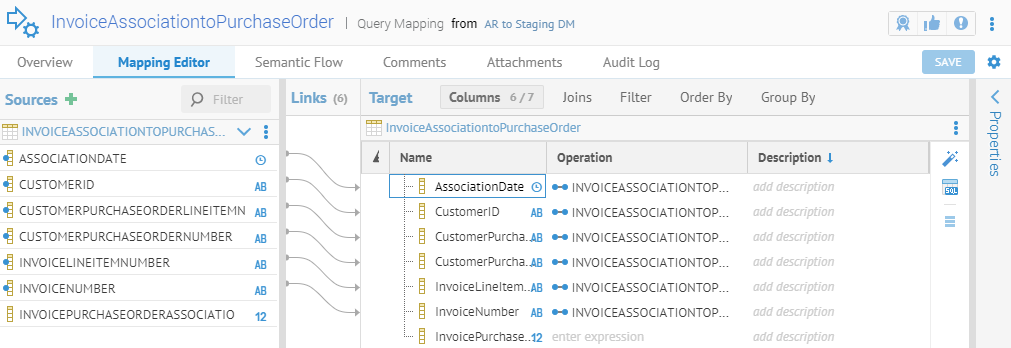
Mapped using a data mapping to the Staging DW model.
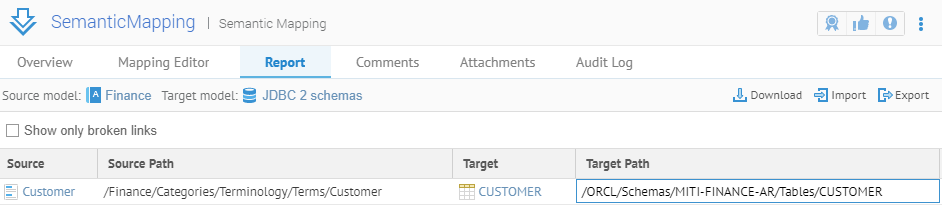
The CUSTOMER table is mapped semantically from the Finance glossary.
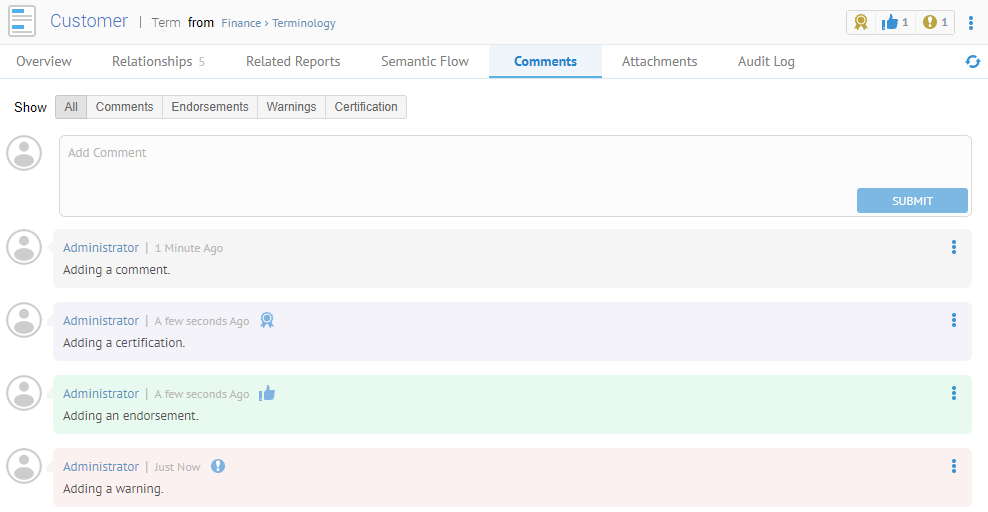
The CUSTOMER table is classified
The CUSTOMER table is commented on, certified, endorsed and warned, and has custom attribution.
Once you have verified that the migration was successful, you may delete the $$Database migration$$ folder which will remove the old single-model populated configurations.
