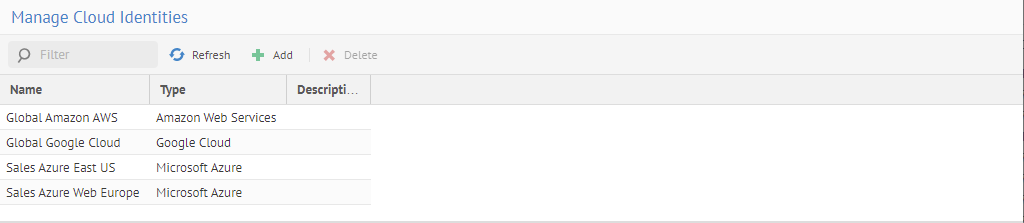

The metadata harvesting (model import) is performed by server (see MANAGE > Servers) that may use allowing secret / password parameters to be based on an external (MetaKarta managed) cloud identity (on Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure) where the secret / password parameter can be:
o A secret identifier which is a URL to a cloud identity secret vault's actual secret (allowing for external storage of such secret / password in a cloud secret vault).
o Empty (no longer mandatory) and the authentication is based on the cloud identity on select bridges (such as Microsoft Azure Data Lake Storage, Microsoft Azure Blob Storage, and more to come).
Public clouds provide identity management and access control infrastructure that enable their customers to define one security principle that can access multiple services using secret-protected or temporary credentials.
For example, Azure allows you to define an identity for an application that can access your storage and database services. MIMM
Public clouds support key vaults that help you to safeguard secrets used by cloud apps and services. Each secret has a unique URL.
Cloud bridges support the following authentication methods:
o Cloud vault secret (sub-method of the cloud identities method)
The bridge decides what authentication method to use based on the presence of values of authentication parameters and logs the decision.