In order to leverage existing LDAP users and ensure that they may use their existing authentication when accessing this product, there is an LDAP authentication mode in MIMM In general, the process is:
1. Set LDAP authentication mode.
2. Configure the connection to your LDAP environment.
3. Optionally configure automated group assignment based upon LDAP attributes.
Once the above is completed, existing LDAP users may simply sign in with their LDAP credentials and they will be identified users in MIMM
Upon external authentication (LDAP), a valid user is created in the system (if not already there) based upon those credentials from the external authentication authority and will then be in MANAGE > Users. Thus, there is no need to import users in these external authentication scenarios.
Steps
1. Sign in as a user with at least the Security Administrator capability global role assignment.
2. Go to MANAGE > Users in the banner.
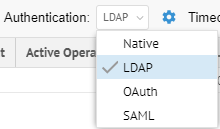
3. Select LDAP from the Authentication pull-down.
Example
Sign in as Administrator.
Go to MANAGE > Users.
Select LDAP from the Authentication pull-down.

As you are altering the methods of authentication which are in effect, you will receive a confirmation dialog.
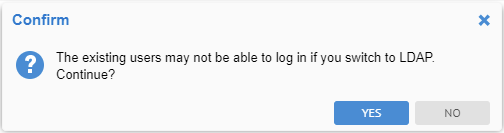
Click YES.
Once you have enabled LDAP authentication, configuration is based upon defining the proper connection to the LDAP server.
Steps
1. Sign in as a user with at least the Security Administrator capability global role assignment.
2. Go to MANAGE > Users in the banner.
3. Be sure LDAP Authentication is enabled.
4. Click the Configure Authentication icon.
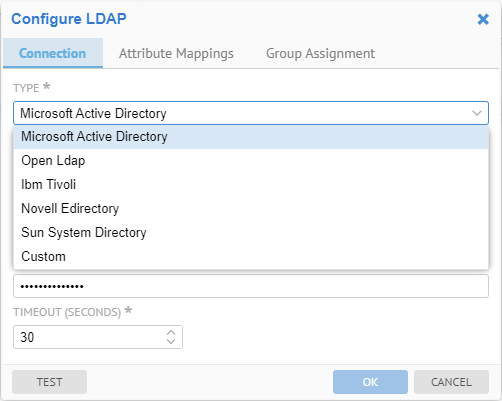
5. Specify the Type of LDAP to be used, which are a set of pre-defined attribute mappings. These include:
o Microsoft Active Directory
o Open LDAP
o IBM Tivoli
o Novell EDirectory
o Sun System Directory
o Custom.
If you select Custom, you may specify further in the Attribute Mappings tab.
With Windows Active Directory, it is generally best to use to the UPN (User Principal Name) format (e.g., USER@FQDN) instead of the Windows domain style (DOMAIN\USERNAME) format (e.g., corp\mc25438. In fact, the Active Directory is configured as a forest, it is mandatory to use the UPN and switch from the default port to the global catalog port as well.
6. Enter the connection parameters available in the Connection tab.
7. Enter the mapping information for LDAP attributes in the Attribute Mappings tab.
8. Use the Test button to validate the settings.
9. Go to the Group Assignment tab to auto-assign groups based upon the LDAP security model.
Example
Sign in as Administrator.
Go to Tools > Administration > Users.
Select LDAP from the Authentication pull-down.

Specify Microsoft Active Directory as the Type of LDAP to be used.
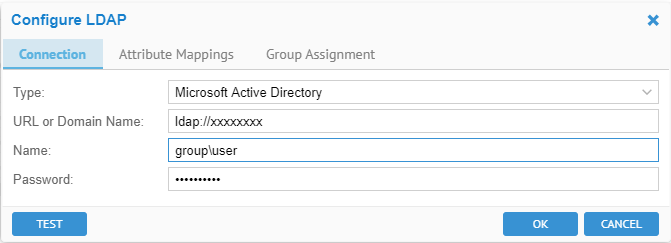
Enter the connection parameters for the LDAP server.
o The URL is generally in the format:
ldap://<server name or IP address>:<port>
o The User and Password are just for testing and configuration purposes.
o Set TIMEOUT (SECONDS)
If you are seeing slow performance when authenticating LDAP users, oftentimes what is taking the vast majority of the time is retrieving the data from the LDAP server. This may often be the case when you are using Microsoft Active Directory on the default port 389. It is recommended to switch to the global catalog on port 3268 (generally the same URL but with the different port).
Click the TEST button to validate the settings.
Go to the Attribute Mappings tab to define user attribute mappings.
Go to the Group Assignment tab to auto-assign groups based upon the LDAP security model.
If you do not click the TEST button, a test connection will be attempted anyway on clicking OK and it must pass successfully before the dialog closes. You may always click CANCEL to cancel the change.
There is no need to create an LDAP user manually. Instead, an LDAP user is automatically created/updated as a result of a successful LDAP authentication login. Thus, all that is required is that the user/password combination is valid for the LDAP authentication connection definitions and query rules.
The LDAP user attributes (login, full name, e-mail, description, etc.) are automatically mapped to selected LDAP attributes (e.g. sAMAccountName is used by default for login on Microsoft Active Directory). In addition, one may change this mapping using the Advanced LDAP connection button.