In order to harvest metadata (model import) from a tool (e.g. database, DI/ETL, BI tool, etc.), the local MetaKarta (Default) Server may not be able to support that tool and therefore require a remote harvesting server (agent) in the following cases:
o a bridge running on Microsoft Windows only (such as COM based tools like SAP BusinessObjects, MicroStrategy), while the MetaKarta Server is running on Linux (on Prem or on Cloud)
o a bridge requiring the tool (often the client) to be installed in order to access its SDK. (such as Oracle DI or Talend DI), while the MetaKarta server is running on the cloud (with no local file system access)
o a bridge requiring access to local files / drivers (such as Database JDBC bridges), while the MetaKarta server is running on the cloud (with no local file system access)
o a bridge connected to a tool running on a different network (such as a MetaKarta server on cloud harvesting from sources on prem).
Go to supported tools for more details on the above requirements:
Installing a remote bridge server is equivalent to installing MetaKarta on an application server, except that one specifies Metadata Harvesting Server Only in the Application Server tab in the setup.bat utility and no license is required and thus it will not have an available web based UI. Please refer to the installation instructions for more details and special instructions for MetaKarta installations in the cloud.
Once such a remote harvesting server is installed and working, one must add it to the list of servers in MetaKarta.
To add a remote harvesting server to MetaKarta.
Steps
1. Sign in as a user with at least the Application Administrator capability global role assignment.
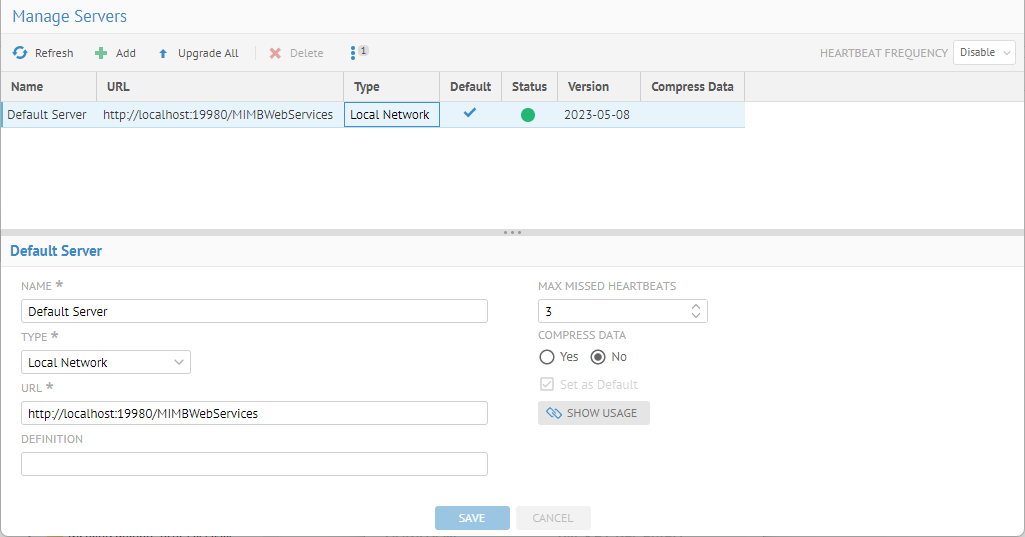
2. Go to MANAGE > Servers in the banner.
3. Specify the HEARTBEAT FREQUENCY.
In order to send out notification when a harvesting server goes down, you must specify a HEARTBEAT FREQUENCY for the application server to check the status of the harvesting servers. By default, this is disabled and no notifications will be sent.
4. Click +Add to add a server or click on the line in the list for an existing server.
5. Specify
6. The Name to refer to this remote server by
7. The Type of remote harvesting server to create
8. Local Network – Remote harvesting server that is within the same domain as the MetaKarta server. In such case, the MetaKarta Server is requesting operations to be performed (in real time when needed) to its registered MIMB Agent. E.g., where the MetaKarta Server is on Linux and needs to import metadata from a MIMB Agent on Windows (for Windows only bridges like Erwin DM, or SAP BusinessObjects).
The default installation of a remote harvesting server does not allow for a Local Network connection for security reasons. You must first use setup.sh -wa MIMBWebServices on that remote harvesting server to be reachable by the main MetaKarta server. For these reasons, it is better to always use Over the Web (Cloud) even if both servers are on the same local network.
9. Over the Web (Cloud) – Remote harvesting server that is local to the organization but the MetaKarta server is Cloud-based. In such case, the MIMB Agent is requesting operation to do on regular basis (every 40s) from its registered MetaKarta Server. E.g., where the MetaKarta Server is on the cloud and needs to import metadata from another Server on prem.
Most operations requested by the MetaKarta server to the MIMB agents are model imports (i.e. metadata harvesting), however a particular operation is to patch the MIMB agent with a MIMB OEM cumulative patch.
10. The URL for this remote server (generally one only need update the machine name inside the URL signature suggested) applies only for Local Network remote harvesting servers. It is of the form
http://<hostname>:<port>/MIMBWebServices
where <hostname> and <port> is the hostname or IP address and port that the remote harvesting server runs on.
11. The SHARED SECRET is used to ensure proper authentication of the remote server by the application server for Over the Web (Cloud) remote harvesting servers. It is a string and must match the M_AGENT_SHARED_SECRET assigned to the remote harvesting server as defined in the agent.properties configuration file. Details about web based configuration is below in the Cloud-based Application Server and Shared Secret section.
Please refer to the installation instructions for more details and special instructions for MetaKarta installations in the cloud.
The M_AGENT_SHARED_SECRET also acts as an identifier, so it must be made unique for a given application server. I.e., each remote harvesting agent must have a unique M_AGENT_SHARED_SECRET. The produce does not use the agent name for anything except for display in the UI.
12. A DEFINITION
13. You may also specify:
14. MAX MISSED HEARTBEATS – to specify the number of missed hearbeats or regular contract from a remote agent before it is considered disconnected
MetaKarta will send out an email notification when a harvesting server goes down, you should specify the MAX MISSED HEARTBEATS. Notification will be sent once the number of missed heartbeats (duration defined as the Heartbeat frequency) is reached, assuming email notification is configured properly.
15. COMPRESS DATA – to use data compression for the communication between the servers
16. Set as Default – To make this remote harvesting server the default when creating models.
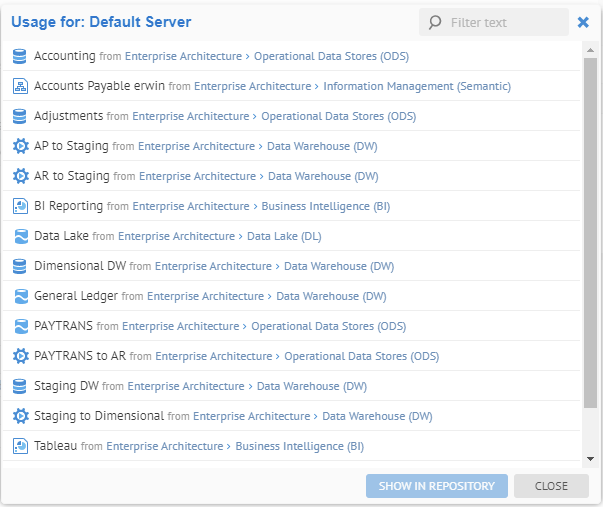
17. You may click SHOW USAGE to see the operations which executed on the selected server.
18. Click Save.
When harvesting using a remote bridge server, one would perform the same steps as for any other harvesting activity with the exception selecting a (remote) Server name in the pull-down.
Examples
Sign in as Administrator and go to MANAGE > Servers.

You may determine the MIMB-OEM patch level in the Version column for each remote harvesting agent and the local (Default) server.
Now, select the line for the Default Server and click Show Usage.
You may now pick this remote agent when creating or updating an imported model.
Explore Further